Psoriasis is a long-term chronic skin disease.
Reasons for disease development
Psoriasis occurs due to the pathology of skin cells. When the top layer of the skin dies within 4-5 days, the time interval is usually several weeks. The cause of the disease is not yet fully understood, but the doctor has identified several factors that cause the disease:
- Genetic susceptibility-The disease appears to be young from the age of 15 and is more likely to be inherited. If one of the parents is diagnosed with psoriasis, the chance of the child getting sick is more than 50%.
- Autoimmune conflict-With this type of disease, the body's immune cells stop recognizing skin cells as part of the body and start attacking them as foreign bodies.
- Neurological shock-promotes the release of hormones into the blood, leading to metabolic disorders and the development of diseases.
- Disrupt hormonal balance and metabolism.
Psoriasis is not contagious because there is no infectious agent that can be transmitted.
Psoriasis symptoms
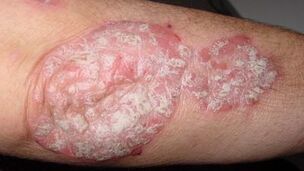
The main symptom of the disease is a characteristic rash on the skin, which mainly affects the inner surface of the elbow and knee joints and the skin areas that are often traumatized by friction.
Skin rashes and other less typical localizations along the edges of the scalp may also occur.
The rash appears in the form of patches covered with gray or white scales. The rash of psoriasis has three characteristics:
- Symptoms of stearic spots:Milky white scales are easy to fall off, and the appearance is similar to candle wax.
- End film-After removing the scale, a whitish film can be seen below it, covering the surface of the spot.
- Spot hemorrhage-When scratching the spot, the end membrane is removed, the skin papilla is damaged, and there is a small drop of blood protruding on it.
In the early stage, a shallow margin is formed around the papules, and no peeling occurs at this stage. The paleness around the spots is the body's vascular response to epidermal rejection. The disease is accompanied by severe skin itching; cracks and light bleeding can form on the skin when scratched. Secondary infections can penetrate through damaged skin.
In addition to the skin, psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing the nail plate to become brittle, with horizontal patterns and concave areas.
Autoimmune conflict can affect the joints and cause arthritis-like pain, especially in the joints of the fingers.
Types of psoriasis
The first type of psoriasis occurs in people under the age of 30. This is a genetic disease that mainly affects the skin and is typically localized.
Type 2 psoriasis affects people over 40 and will not be inherited. It usually affects the nail plate and scalp, and the rash is small and teary. Elderly patients’ diseases are caused by decreased immunity to chronic infectious diseases and poor lifestyles.
Clinical studies have shown a link between type 2 psoriasis and alcohol and unhealthy food abuse.
Forms of psoriasis
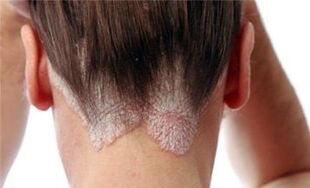
Psoriasis has several forms of varying severity:
- Plaque psoriasis-characteristic papules are formed on the skin, accompanied by itching and peeling.
- The pustule formis characterized by the appearance of air bubbles, redness of the surrounding skin, severe itching and burning, and is considered a moderate form of the disease.
- Erythrodermais characterized by extensive skin lesions, accompanied by large layers of epidermis exudation and drainage, which are particularly difficult to tolerate, usually accompanied by pustular lesions and fungal infections.
Stages of psoriasis
This disease develops in several stages:
- Initial stagemeans the onset of the disease. During this period, one (rarely) several light spots appear and the skin begins to fall off.
- Active periodAccompanied by severe symptoms, a large amount of skin scaly discharge, itching and inflammation.
- Stationary Phase-indicates remission, the peeling at this stage actually stops, instead of forming spots, pigmentation or pale pseudo-shrinking areas.
Psoriasis diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a dermatologist. The pathology has clear clinical images, which was confirmed by autopsy and biopsy of his corpse and subsequent studies.
Psoriasis treatment
The disease should be treated comprehensively while stopping the external symptoms and affecting the possible causes of the disease.
Medications
In severe cases, measures will be taken to reduce the body’s immune attack on its own cells:
- Cell inhibitors;
- Antihistamines;
- Corticosteroids;
- Intestinal absorbers and hepatoprotectants are used to restore metabolism.
At the same time, measures are being taken to make the human body contain essential vitamins and trace elements:
- Silicon is one of the important trace elements responsible for hormone balance and skin health.
- Calcium and vitamin D3 are essential to alleviate the disease. Prescription together can increase calcium absorption.
Local treatment
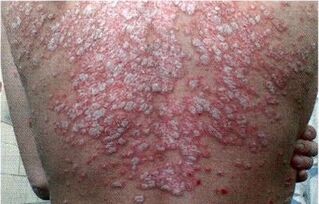
To protect the skin, the topical agent is used in the form of ointment and cream:
- Glucocorticoids reduce the immune response, also reduce inflammation symptoms, reduce skin itching and swelling.
- Salicylic acid and herbal products are essential for moisturizing the skin and preventing secondary infections.
- Local cytostatic drugs are only used during the active phase of the disease and its severe course.
Process
In order to speed up the healing process, physiological procedures are prescribed:
- cryotherapy;
- Ultraviolet radiation;
- Laser processing.
If necessary, perform plasma exchange to purify plasma and stabilize cells.
Prevention
If the susceptibility to the disease is determined, a variety of preventive measures must be taken:
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking and alcohol;
- Establish daily work, avoid stress, and arrange work schedule reasonably;
- Avoid excessive carbohydrates, spices and high-fat foods in your diet. It is recommended to avoid the use of preservatives and fast food;
- Spend enough time outdoors;
- Use soap and shampoo with a specially selected pH value. Do not use hard towels and towels. Dry your skin thoroughly after showering;
- Wear clothes made of natural materials that are not too close to the body;
- Regular medical examinations to control the level of hormones in the blood, and start early treatment if necessary.
These measures will help maintain healthy skin and significantly improve the quality of life.























